- They are anti adrenergic drugs which block the alpha and beta receptors present throughout our body .
- All the alpha receptors have excitatory action except in the GIT
- All the beta receptors have depressant action except on heart
- Alpha receptors - type 1 and 2
- Type 1 are responsible for - vasoconstriction, smooth muscle contraction( in GIT cause relaxation ) learning etc
- Type 2 are preganglionic have inhibitory control
- Major uses of alpha blockers are in management and diagnosis of pheochromocytoma , in management of benign prostatic hyperplasia
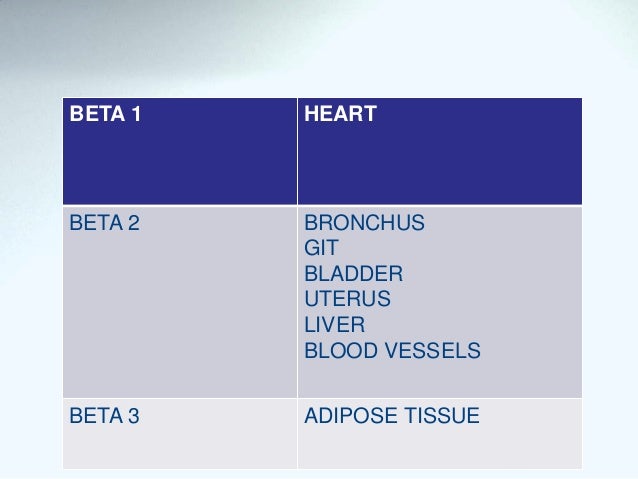
- Beta receptors -Type 1,2,3
- Type 1 - present in heart and their stimulation results in increased heart rate , increased force of contraction, increased speed of conduction of impulse from SA node to AV node.
- Type2 - their stimulation is responsible for vasodilation, bronchodilation, smooth muscle relaxation etc
- Type 3 - present on fat cells , exact function is not yet completely understood.
- Major use of beta blockers is in management of hypertension and in preventing remodelling of heart incase of heart failure
the above functions in a tricky chart is given below:-

from above actions,we can conclude that:-
Alpha = Constrict.
Beta = Dilate

BLOCKERS
ALPHA-BLOCKERS

BETA-BLOCKERS
Beta blockers, also written β-blockers, are a class of medications that are particularly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack (myocardial infarction) after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients.
Beta-blockers site of action ( remember of 1 heart , 2 lungs)Beta-1 = 1 heart
Beta-2 = 2 lungs

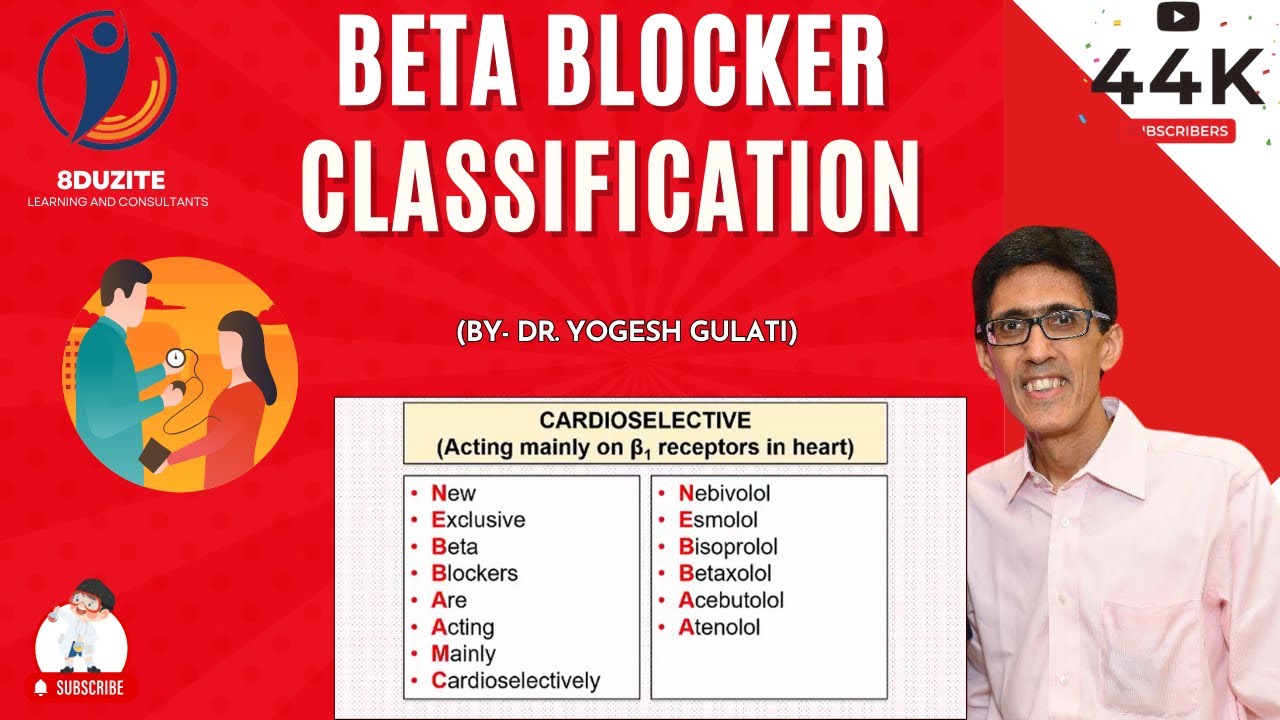
Beta blockers: B1 selective vs. B1-B2 non-selective (remember of A->N O->Z)
A through N: B1 selective: Acebutalol, Atenolol, Esmolol, Metoprolol.
O through Z: B1, B2 non-selective: Pindolol, Propanalol, Timolol.
Uses of Beta-blockers include (remember of H&M HAT):
Hypertension / Hypertension ocular (Glaucoma)Myocardial infarction /Migraine prevention
Hyperthrophy obstructive cardiomyopathy
Angina pectoris / Arrhythmia
Thyrotoxicosis

Beta-blockers: main contraindications, cautions (remember of ABCDE):

Beta-blockers: side effects (remember of "BBC Loses Viewers In Rochedale"):
BradycardiaBronchoconstriction
Claudication
Lipids
Vivid dreams & nightmares
Inotropic action
Reduced sensitivity to hypoglycaemia


mnemonic for mixed: CARme LAB
INTERESTING FACTS
- Atenolol is longer acting than propranolol and generally has fewer side effects. It has less of a tendency to produce wheezing than other beta blockers. Once-a-day dosing is convenient.

- Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a chronic progressive condition that affects the pumping power of your heart muscles.
- ATENOLOL
- PROPRANOLOL

- TIMOLOL


No comments:
Post a Comment